If you were to walk down the street and ask ten people what their most-valuable financial asset is, there is a good chance that all ten would point to assets such as a house, cottage, or investment portfolio. However, if you think about it, your most valuable asset is your ability to earn an income. Why? Because the ability to earn an income is what makes everything else possible.
Small business owners, independent contractors, freelancers, gig workers – no matter where you fall on the self-employment spectrum, disability insurance is imperative.
And with 40% of Canadians becoming disabled for 90 days or longer before the age of 65[1], purchasing disability insurance for the self-employed in Calgary is a strategic and smart move. Click here to learn about your risk of experiencing an illness that can render you unable to work.
What If You Suddenly Lost Your Income due to Sickness/Injury?
Without disability insurance to help cover expenses, many people would find themselves in financial trouble. “There is a mistaken perception that disabilities tend to be catastrophic in nature caused by one-time, traumatic events. Most Canadians don’t recognize that common, chronic conditions such as mental illness cause the majority of disabilities. In fact, less than 10% of disabilities are caused by accidents,” said RBC’s Mark Hardy in a press release.
Being off work with a disability can take a heavy toll on individuals and families. Not only are you coping with your disability and trying to get better, but the financial and emotional stress affects everyone in the family.
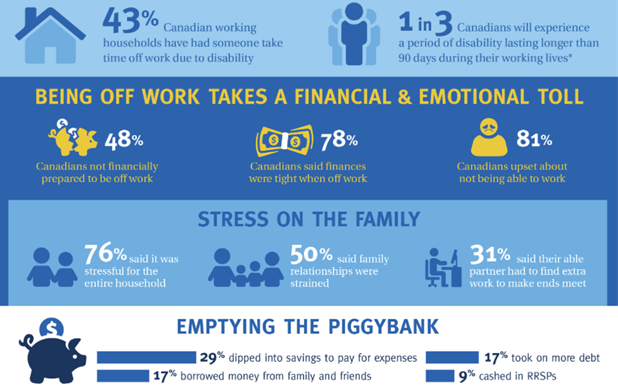
What about EI, WCB, or Canada Pension Plan?
Government programs like the Canada Pension Plan (CPP), Employment Income (EI), and Workers’ Compensation (WCB) can help when you become disabled and unable to work, but you will need to meet certain conditions to qualify.
- CPP – The eligibility for this is very strict, you must “have a severe and prolonged mental or physical disability” to qualify for CPP disability benefits. The maximum benefit is approximately $900/month.
- WCB – Only covers on-the-job accidents and, depending on your industry, many self-employed do not have coverage. An injured worker can receive 90% net of their compensable earnings up to a set limit, depending on the year and the province.
- EI – As this is optional, not all self-employed pay into this program. However, if you do pay into it, the maximum amount you can receive is 55% of your average insurable weekly earnings, up to a maximum amount (as of 2022 it was $638/week). The benefit is received for the short term only, 14 weeks up to a maximum of 45 weeks, depending on the unemployment rate in your region.
Types of coverage for the self-employed
Assuming you do not have employees, there are basically two types of coverages available: business overhead and income replacement. You can purchase these independently of or in conjunction with each other. If you have employees or business partners you can read our other article, disability insurance for the small business for more options.
Overhead expense plan
This policy covers eligible business expenses during total disability. This option is best for owners with monthly expenses with a payout of 1 or 2 years. It helps you retain valued staff, pay ongoing expenses, and avoid disruption to your business. It is most vital for businesses and practices in which the owner’s ability to generate income makes the difference between the office being open or closed for business—for example, sole proprietors, physicians, lawyers, accountants, engineers, and others.
Loan/credit insurance
Being self-employed, not all your expenses are business owned. For example: the car you use for work is your personally owned vehicle. This coverage protects all your personal (not business) loans in case of disability and helps you keep making payments. Your benefits are not integrated, which means that they’re paid directly to you, even if you receive other disability insurance benefits, they are paid in addition to those. You can use it to cover several loans: mortgage (or rent), credit card, line of credit, student loan, car loan or rental, etc. The loans covered can be changed as your situation evolves over time.
Income replacing plan
This can provide long and short-term disability coverage if you are unable to work due to injury and/or illness. Disability insurance can help you and your family pay for necessary expenses like your mortgage, car payments, utilities, and groceries. The benefit amount you can receive while disabled is a percentage of your pre-disability income. For example, If you earn $50,000 per year, you may be eligible to receive a monthly tax-free benefit of $2,975, giving you a take-home pay of nearly $36,000. If you earn more, such as $120,000, you could qualify for a monthly benefit of just under $6,000, giving you a tax-free take-home pay of $71,100.
How much are you eligible for?
How much disability benefits you can buy depends on how much you earn. The more you earn, the higher the benefit you can get. If you pay yourself a salary, the calculation is easily based on your T4 slips. However, for the self-employed it can be harder to calculate as income is not always consistent, you may pay yourself in dividends, etc.
The insurance companies each have their own calculations and allowable income sources but in general, you can include salary, fees, bonuses, and commissions, as well as a portion of a corporation’s net income before taxes. The self-employed can also be eligible for a 20% top-up to their T4 statements to account for the expenses that are written off against reported income. For example, if you earned $100,000, you can increase this to $120,000 and buy $5,925 in monthly benefits instead of $5,200.
How does disability insurance work?
The cost of a disability insurance policy depends on factors like your age, gender, occupation, income, and plan design.
- Choose the coverage amount you want.
- Add optional benefits to customize your coverage.
- Pay the monthly premium.
- File a claim if you become disabled.
- Receive your monthly payments when the waiting period ends. The waiting period is the number of days from the date you’re disabled until the benefits start date.
- Your payments stop when your benefit period ends or you return to work.
Without question, people who are self-employed in Canada represent a diverse, dynamic, and rapidly growing group with unique needs. This also comes with more responsibility – don’t let an injury or an illness derail everything that you’ve worked hard to build.
Why wait? If you don’t have disability insurance for the self-employed, now is the time to contact our business advisory team to protect yourself, your family, and the future of your business.
Read our article on What should I look for in a disability policy for more information on the options available.
[1]Canada Life (2022)

