Every private Canadian business has a tax account that is particularly valued by shareholders: the capital dividend account (CDA). What is so important about the CDA? When its balance is positive, it offers an exceptional tax advantage: to be able to withdraw a corporation’s money without paying any taxes.
The Capital Dividend Account (CDA) is a notional account, not a literal account. In the same way that your RRSP room keeps track of your unused RRSP contribution room, your CDA keeps track of the amount of money your private corporation can pay out as a tax-free capital dividend … this means that small businesses can pay out tax free money to its shareholders through the CDA.
The CDA is available to private corporations for the purpose of tracking certain tax-free surpluses, such as:
- The tax-free portion of capital gains & losses
- The tax-free portion of dispositions of eligible capital property (such as goodwill)
- Capital dividends received from other corporations
- Life insurance proceeds received by the corporation as beneficiary on the death of the life insured
Here is a general idea of how they work:
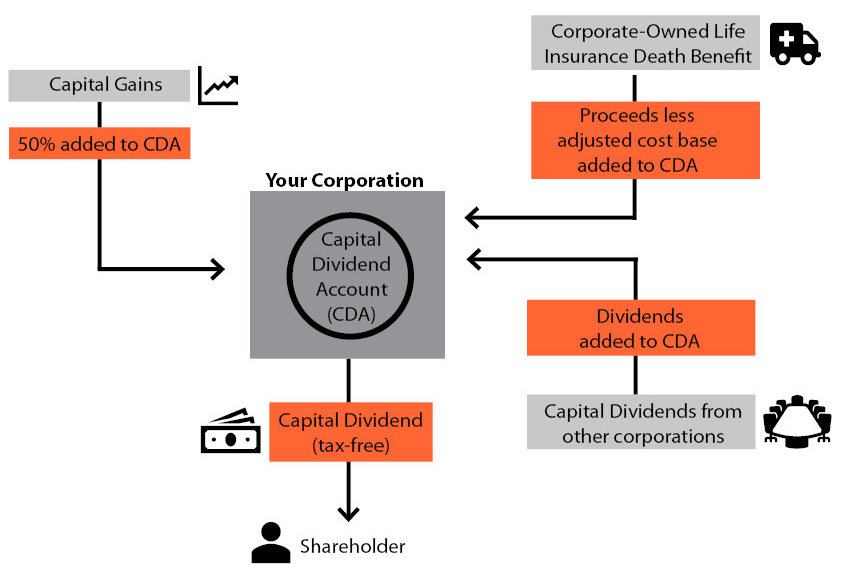
As discussed, the CDA is a notional account that is only relevant for tax purposes. You won’t see it generally included on the balance sheet of the company, although it may be included in a footnote to the financial statements. Your accountant should be able to provide you with your corporation’s CDA balance.
Are CDA’s approved by Canada Revenue Agency?
This is not an error or an oversight by tax authorities. On the contrary, the CDA exists precisely to enforce a major taxation principle: integration. This principle requires that every individual pays a relatively equal tax, regardless of whether their income is earned directly or through a company.
As profits have already been taxed as business revenue, it would be unfair—under the principle of integration—to fully tax them a second time once these profits are transferred to shareholders as dividends. Considering that the first tax is paid by the company, the second tax—paid by the shareholder who receives the dividend—is therefore at a reduced rate.
Life insurance within a corporation
A corporation can be a beneficiary of a life insurance policy. This generally allows the corporation to pay the premiums for that policy and collect proceeds upon the death of the covered person. In most cases the premiums are not deductible; however, they can still be paid using corporate dollars which are at a lower tax rate than using after-tax personal dollars.
Upon death of the insured person, the insurance company will pay the death benefit tax-free to the corporation and an equivalent amount (net of any adjusted cost basis) is added to the company’s CDA This amount can then be paid out tax free to shareholders as a capital dividend.
Investments within a corporation
Many business owners have the decision to keep money within their corporation (as retained earnings) or to withdraw it as income or dividends. Retained earnings are a mixed blessing for business owners. On one hand, they represent the company’s success and profitability. On the other hand, it can be a challenge to take those earnings out of the business without incurring a large tax bill.
This is where an investment within the corporation can help.
As the investment grows in value, the profits it generates is taxable. The amount of taxes paid depends on the type of income earned, such as interest income, dividends, or capital gains. You can structure the investments to only create capital gains and dividends. This is where the CDA is a valuable asset: the capital gain. When a capital gain is generated (from the sale or disposal of an investment), only 50% of the gain is subject to a tax. The non-taxable portion of the gain is then added to the capital dividend account (CDA).
Then, when it is time to withdraw money from the corporation, the corporation declares a tax-free capital dividend up to the amount of the CDA balance. As an extra benefit for the shareholder of the company, this tax-free distribution doesn’t impact government benefits such as Old Age Security.
Donating securities
A corporation can also donate certain eligible securities directly to registered charity. This can be an effective donation strategy if the corporation has investments with large accrued capital gains. The corporation can deduct the full fair market value (FMV) of the investment donated to a registered charity against its income, reducing overall taxes payable. In addition, the capital gain on the securities donated to a registred charity may be eliminated and the full value of the capital gain is added to the corporation’s CDA. This increases the amount that can be paid tax-free to the corporation’s shareholders.
Next steps
What should you do with this information? Ask your tax accountant to verify your current CDA balance. Next, you should tax with a financial planner to see if any of these options are strategies you can use. Many financial planners specialize in corporate planning are also happy to liaise between your investment advisor and tax accountant to co-ordinate tax-free withdrawals in harmony with your planning needs.

